Signature of an anticipatory response in area V1 as modeled by a probabilistic model and a spiking neural network
Abstract
As it is confronted to inherent neural delays, how does the visual system create a coherent representation of a rapidly changing environment? In this paper, we investigate the role of motion-based prediction in estimating motion trajectories compensating for delayed information sampling. In particular, we investigate how anisotropic diffusion of information may explain the development of anticipatory response as recorded in a neural population to an approaching stimulus. We validate this using an abstract probabilistic framework and a spiking neural network (SNN) model. Inspired by a mechanism proposed by Nijhawan [1], we first use a Bayesian particle filter framework and introduce a diagonal motion-based prediction model which extrapolates the estimated response to a delayed stimulus in the direction of the trajectory. In the SNN implementation, we have used this pattern of anisotropic, recurrent connections between excitatory cells as mechanism for motion-extrapolation. Consistent with recent experimental data collected in extracellular recordings of macaque primary visual cortex [2], we have simulated different trajectory lengths and have explored how anticipatory responses may be dependent on the information accumulated along the trajectory. We show that both our probabilistic framework and the SNN model can replicate the experimental data qualitatively. Most importantly, we highlight requirements for the development of a trajectory-dependent anticipatory response, and in particular the anisotropic nature of the connectivity pattern which leads to the motion extrapolation mechanism.
- Based on(2012). Motion-based prediction is sufficient to solve the aperture problem. Neural Computation.
- see follow-up on motion extrapolation:(2013). Motion-based prediction explains the role of tracking in motion extrapolation. Journal of Physiology-Paris.
- see follow-up on the flash-lag effect:(2017). The flash-lag effect as a motion-based predictive shift. PLoS Computational Biology.
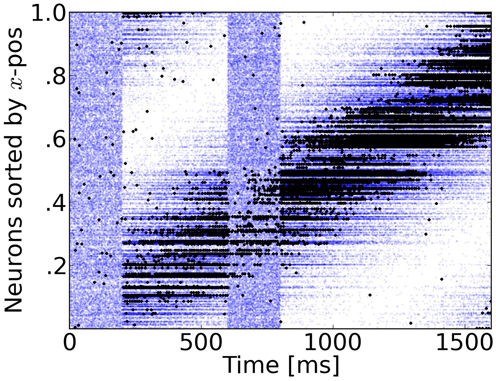
Figure 4: Rasterplot of input and output spikes. The raster plot from excitatory neurons is ordered according to their position. Each input spike is a blue dot and each output spike is a black dot. While input is scattered during blanking periods (Figure 1), the network output shows shows some tuned activity during the blank (compare with the activity before visual stimulation). To decode such patterns of activity we used a maximum-likelihood estimation technique based on the tuning curve of the neurons.